The Importance of Neuroimaging and Neuroradiology in Diagnosing Brain Disorders
Explore the role of neuroimaging in diagnosing brain disorders, uncovering how advanced imaging techniques enhance accuracy, guide treatment, and transform patient outcomes.
Neuroimaging and Neuroradiology: Essential Tools in Modern Medicine
Neuroimaging is an essential tool in the modern medical field, especially for understanding and diagnosing brain disorders. With the advancement of technology, neuroimaging techniques have evolved, providing insights that were once inaccessible.
Neuroradiology, a subspecialty within this field, focuses specifically on using these imaging techniques for diagnosing and characterizing neurological conditions.
Understanding Neuroimaging and Neuroradiology: A Brief Overview
Neuroimaging encompasses a variety of techniques that create visual representations of the brain’s structure and function. These techniques, pivotal in both research and clinical settings, have revolutionized our understanding of neurological conditions. Neuroradiology applies these brain imaging techniques in clinical practice, assisting neuroradiologists in diagnosing and monitoring brain disorders.
The primary objective of neuroimaging is to enhance our knowledge of brain function and structure, while neuroradiology aims to utilize this imaging to diagnose brain disorders, assess their severity, and monitor changes over time.
For instance, neuroimaging has played a crucial role in research settings by identifying biomarkers for diseases such as Alzheimer’s and multiple sclerosis, allowing for earlier intervention and more personalized treatment plans. Meanwhile, neuroradiology directly supports clinical decision-making in healthcare settings.
Different Types of Brain-Imaging Techniques and Their Clinical Application in Neuroradiology
Several neuroimaging techniques serve distinct purposes, with some particularly aligned with neuroradiological practices:
Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI): Provides detailed images of brain structures.
Functional Magnetic Resonance Imaging (fMRI): Measures brain activity by detecting changes associated with blood flow.
Computed Tomography (CT) scans: Offers quick images of the brain and is often used in emergency settings.
Positron Emission Tomography (PET): Assesses metabolic processes in the brain.
Electroencephalography (EEG): Used for mapping brain activity, EEG measures electrical activity in the brain through electrodes placed on the scalp.
Each technique provides unique insights into the brain and its functions, making them invaluable in diagnosing and managing various disorders.
Enhance Neuroradiology Learning with advanced imaging software and infinite anatomies
The Pivotal Role of Neuroimaging in Enhancing Neuroradiology for the Clinical Diagnosis of Brain Disorders
Neuroimaging is a cornerstone in modern medical diagnostics, playing a transformative role especially within the field of neuroradiology, where it is essential for the clinical diagnosis of brain disorders.
These advanced imaging techniques provide an unparalleled view of the brain’s structure and function, enabling neuroradiologists to uncover and understand complex neurological conditions with exceptional detail and accuracy.
By utilizing neuroimaging, neuroradiologists can make precise diagnoses, detect subtle pathologies, and define the extent of diseases. This high level of diagnostic precision is critical for developing targeted treatment plans and implementing effective medical interventions.
In the field of neuroradiology, neuroimaging is not just beneficial; it is indispensable, serving as the backbone for accurate assessments and better patient outcomes in the increasingly complex landscape of healthcare.
Neuroimaging and Neuroradiology in Diagnosis
Neuroimaging, as applied through the specialty of neuroradiology, is crucial in the clinical diagnosis of brain disorders. These techniques enable the capture of detailed images of the brain, allowing both healthcare providers and neuroradiologists to make informed, data-driven decisions.
For instance, Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) can reveal structural changes associated with conditions such as multiple sclerosis or traumatic brain injury, while functional MRI (fMRI) provides insights into functional abnormalities that occur in disorders like schizophrenia.
This capability to visualize both structural and functional aspects of the brain empowers medical professionals to conduct precise diagnoses and plan effective medical interventions.
By leveraging the comprehensive data provided by neuroimaging, neuroradiology enhances the accuracy of diagnoses and supports targeted treatment strategies, ultimately improving patient care.
Monitoring Disease Progression Through Nuromimaging and Neuroradiology
Beyond diagnosis, neuroradiology is instrumental in monitoring the progression of brain disorders.
By regularly assessing changes in brain structure or function, physicians can gauge the effectiveness of treatments and make necessary adjustments, ensuring that patient care is as effective as possible.
In chronic conditions such as Alzheimer’s, neuroimaging can provide crucial information about the progression of the disease, offering insights into the timing of interventions or changes in care strategies.
Neuroimaging can also be utilized in clinical trials to evaluate the efficacy of new therapeutic approaches, allowing researchers to observe how treatments impact brain activity and structure over time.
ReMIND Brain 2.0 MRI Scan, screenshots taken in 3DICOM MD.
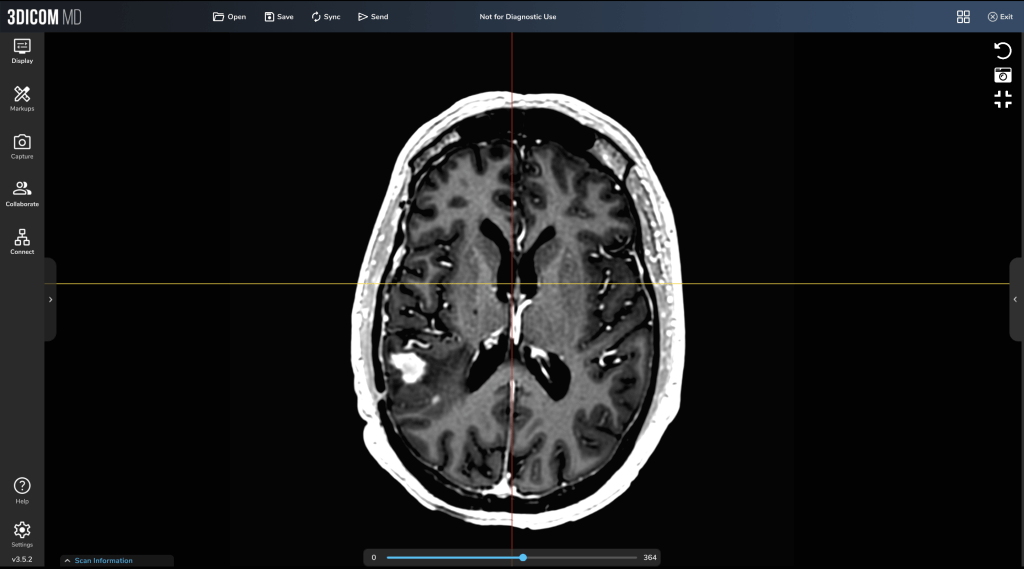
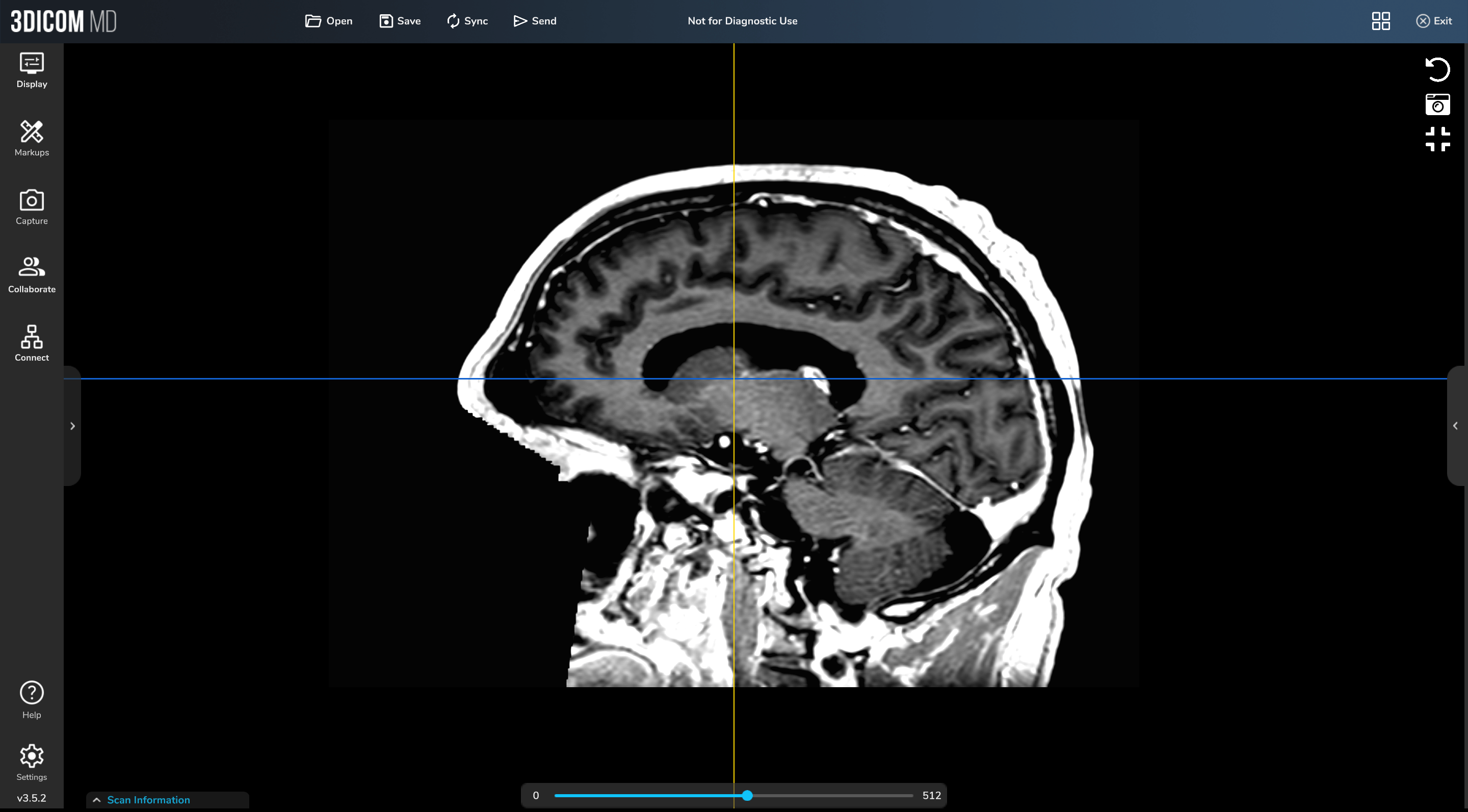
The Impact of Neuroimaging and Neuroradiology on Personalized Treatment Planning
Personalized Diagnostic Insights
The insights derived from neuroimaging, enhanced through its clinical application in neuroradiology, play a critical role in shaping personalized treatment plans for patients with brain disorders. These advanced diagnostic tools provide invaluable data that enable healthcare professionals to tailor therapies precisely to the unique characteristics and dysfunctions observed in patient scans. For example, the specific location and type of a brain tumor revealed through imaging can significantly influence decisions regarding the most appropriate surgical approach or radiation therapy plan.
Monitoring and Adjusting Treatment
Moreover, neuroimaging allows for the continuous monitoring of how a patient’s brain responds to ongoing treatments, facilitating timely adjustments in medication dosages or changes in therapeutic strategies. This dynamic approach ensures that treatment plans remain aligned with each patient’s evolving condition, enhancing the effectiveness of interventions and significantly improving outcomes.
Enhancing Treatment Outcomes through Neuroimaging
By integrating neuroimaging into the core of treatment planning, neuroradiology ensures that medical interventions are based on the most accurate and comprehensive understanding of brain pathology. This integration not only improves the quality of life for patients but also paves the way for more targeted and successful therapeutic outcomes.
The Future of Personalized Medicine
As we advance into an era where precision medicine is increasingly important, the roles of neuroimaging and neuroradiology are becoming critical. The integration of neuroimaging into personalized medicine is not just a trend but a future necessity.
Emerging techniques and continuous improvement of existing methods offer unparalleled insights, allowing for tailored approaches to treatment that consider an individual’s unique brain structure and function. This patient-centric model is reshaping how we approach brain health, with neuroradiology at the forefront of clinical application.
The application of machine learning and AI in analyzing neuroimaging data is poised to revolutionize treatment planning. These technologies can identify subtle patterns that may not be visible to the human eye, leading to earlier diagnoses and more effective treatment strategies.
The Future of Diagnosing Brain Disorders
The future of neuroimaging in diagnosing brain disorders looks promising, primarily due to rapid advancements in technology and research. These advancements are changing how we understand and treat brain disorders.
ReMIND Brain 2.0 MRI Scan, screenshots taken in 3DICOM MD.
Emerging Technologies and Their Application
Recent innovations in neuroimaging, such as high-resolution imaging and ultra-fast MRI scanning, enhance the ability to view the brain in real-time – offering insights that were previously unimaginable – which are crucial for both research and clinical practice.
Moreover, developments in functional neuroimaging techniques provide a better understanding of cognitive processes and disorders, leading to earlier diagnoses, improved treatment protocols, and better overall patient outcomes.
These advancements can lead to earlier diagnoses, improved treatment protocols, and better overall patient outcomes.
Essential Tools in Modern Medicine:
- Neuroimaging is vital for understanding and diagnosing brain disorders.
- Neuroradiology, a subspecialty of neuroimaging, focuses on diagnosing and characterizing neurological conditions using these imaging techniques.
Overview of Neuroimaging and Neuroradiology:
- Neuroimaging includes various techniques that visualize the brain’s structure and function.
It plays a crucial role in both research and clinical settings, enhancing our understanding and management of neurological conditions. - Neuroradiology applies these techniques in clinical practice for diagnosing and monitoring brain disorders.
Techniques and Their Clinical Applications:
- Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI): Provides detailed images of brain structures.
- Functional Magnetic Resonance Imaging (fMRI): Measures brain activity by detecting changes in blood flow.
- Computed Tomography (CT): Offers quick images, often used in emergencies.
- Positron Emission Tomography (PET): Assesses metabolic processes in the brain.
- Electroencephalography (EEG): Measures electrical brain activity via scalp electrodes.
Each technique offers unique insights, crucial for diagnosing and managing disorders.
Enhancing Clinical Diagnosis through Neuroimaging:
- Neuroimaging is indispensable in neuroradiology for clinical diagnosis.
- It allows for precise diagnoses, the detection of subtle pathologies, and defining disease extent.
Role in Diagnosis:
- Neuroimaging enables detailed brain imaging, crucial for informed, data-driven decisions by healthcare providers and neuroradiologists.
- Techniques like magnetic resonance imaging and functional MRI (fMRI) can reveal structural and functional abnormalities, essential for accurate diagnosis and treatment planning.
Monitoring Disease Progression:
- Neuroradiology is key in monitoring the progression of brain disorders and assessing changes in structure or function over time.
- Useful in chronic conditions like Alzheimer’s disease for tracking disease progression and adjusting care strategies.
Impact on Personalized Treatment Planning:
- Neuroimaging data is critical for tailoring treatment plans to individual patient needs.
- Allows ongoing monitoring of treatment responses, enabling adjustments to therapies based on evolving patient conditions.
Future of Personalized Medicine and Neuroimaging:
- As precision medicine advances, neuroimaging and neuroradiology become increasingly integral.
- Emerging imaging techniques and AI applications in neuroimaging are set to revolutionize diagnosis and treatment planning, enhancing early diagnosis and treatment efficacy.
Emerging Technologies and Their Impact:
- Innovations like high-resolution and ultra-fast MRI scanning improve real-time brain imaging capabilities.
- Developments in functional neuroimaging enhance understanding of cognitive processes and disorders, leading to improved treatment outcomes.